
The Essence of DeFi
Since the beginning of the practical blockchain product development, a little more than 10 years have passed, but during this time there has been a significant technological and informational leap in the development of the crypto sphere. The terminology and many concepts in this rapidly developing industry are still at the stage of formation and refinement; completely new definitions appear as a result of the establishment of a new trading field.
DeFi is one of the blockchain evolutions. Its ecosystem is growing and developing, striving for status as one of the key constituents in the field of cryptocurrency finance. Financial independence and the absence of intermediaries in important financial transactions are key features that provide this market with the potential for exponential growth.
What is DeFi?
Cryptocurrencies have allowed people to refuse interactions from a crowd of centralized intermediaries in the transfer of value, leaving the accounting operators (miner, block producer, and delegate) out of the process. This has served as a powerful impetus for the development of both technology and financial relationships. The transfers of tokens gained momentum and, with the growth of the total capitalization for the market, they shot into the modern world of finance. DeFi stands for open tools or protocols in distributed systems that solve some financial problems.
DeFi stands for Decentralized Finance – the most massive use of tokenization. It is an ecosystem that has emerged from the rise of many different types of blockchain-built financial applications. DeFi is a movement aimed to decentralize the traditional centralized financial services industry.
Analysts distinguish several main categories of DeFi:
- Decentralized Exchanges (the so-called distributed exchanges, also known as DEX) and open exchange protocols (UniSwap, Kyber Network, Bancor Network, Ren, IDEX, and BitShares);
- Lending and Borrowing (MakerDAO, Compound, Dharma);
- Derivatives, Margin Trading & Prediction Markets (Augur, CDx, dYdx, bZx, and Daxia);
- Liquidity Mining (SushiSwap, Pickle, Cream Finance, Core Vault, and others).
A feature of DeFi development company in a single distributed system is the ability of protocols to interact with each other and with derivative tokens. That is why DeFi on the Ethereum blockchain gained the most popularity.
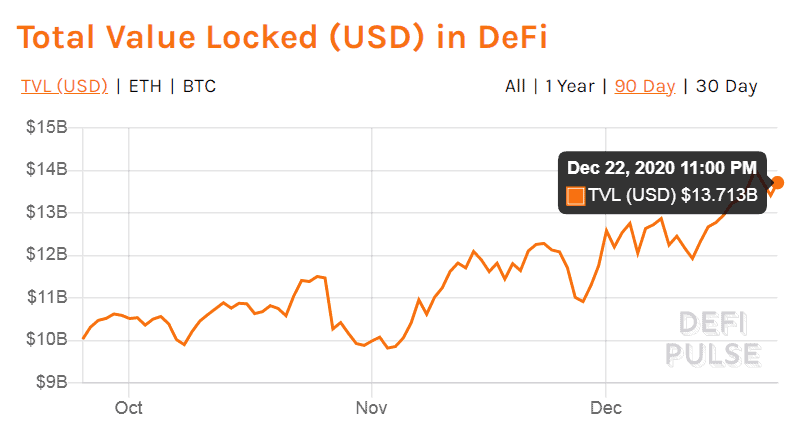
Source: DeFi Pulse
But against the backdrop of blockchain integration services and tools, something else is happening: the existing financial world is preparing to enter the game in the market of distributed ledger systems. In many large companies, hundreds of thousands of DeFi developers are working to serve the transfer needs of modern humanity. Development is carried out in many directions:
- Insurance
- Identification
- Metal Trade
- Clearing House
- Patents
- Healthcare/Health Insurance
- Crediting
All of these are no longer just prototypes; they are real services that are waiting for clients who are ready to plunge into the universe of decentralized finance.
Technology Overview
DeFi operates on the basis of smart contracts – the best blockchain technology application that exists in the world. Blockchain is a decentralized database, in which all records are formed into blocks organized in a linear order. Moreover, each subsequent block absorbs all the previous information of its predecessor. Nodes (users) must have some influence in order to be able to add records (transactions) to the database, while the process of recording the database itself must use certain resources to ensure the operation of all nodes.
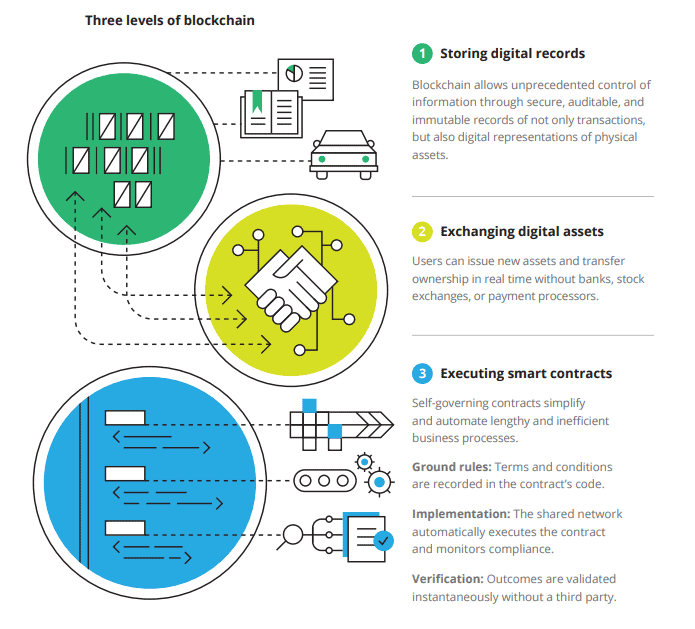
source: Deloitte
Blockchain technology guarantees the security and uninterrupted operation of a distributed network, using cryptocurrencies and tokens for the exchange of values. Therefore, cryptocurrencies (or tokens), like digitized fiat money, are used to display the value of certain transactions that are created by users in a decentralized network. At the same time, the rules for organizing money issues in the blockchain product development system are always determined by the computer code of free software of a particular cryptocurrency and not by the will of the government or the central bank.
Technical Analysis
The DeFi apps are built around a series of smart contracts – their “if this, then that” logic governs the behavior of assets in the ecosystem. Smart contracts eliminate the need for centralized intermediaries, thereby reducing the cost and processing time of financial transactions. This technology simplifies processes so much that they are even used by centralized suppliers to improve their efficiency.
The DeFi ecosystem is usually rendered and explained as a collection of layers. Opinions differ on the number of layers and how they are designated, but it is generally accepted that the base layer is the blockchain on which it is built (almost always Ethereum). So, DeFi consists of five layers: the settlement layer, the asset layer, the protocol layer, the application layer, and the aggregation layer.
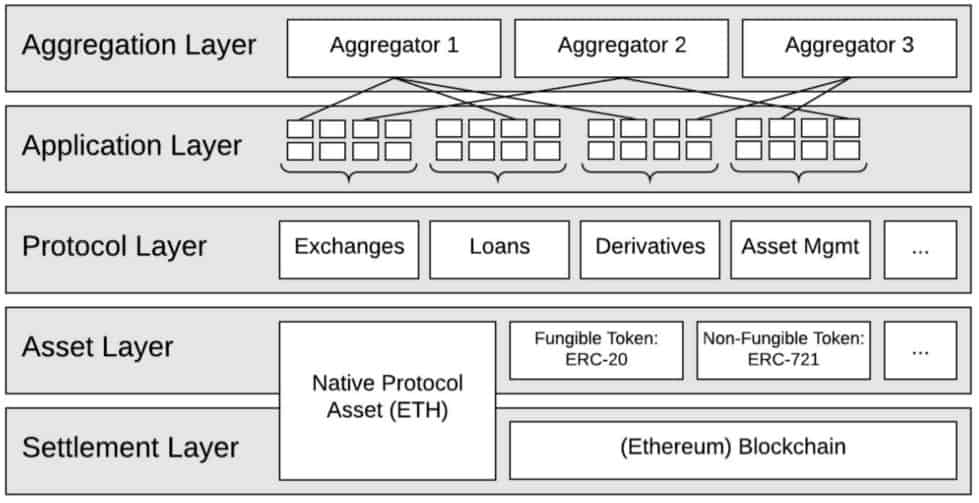
Visualization of DeFi Layers, source: ResearchGate
So, DeFi works on 5 layers. Each of these layers has a separate aim:
The settlement layer is the one that underlies blockchain itself. Without this foundation, there won’t be anything to build apps on. It is a base that works differently than anything in the world of centralized finance: transactions are confirmed by miners and recorded in the blockchain’s distributed ledger. This unique functionality, though, has several potential drawbacks related to transaction costs and the time needed to conduct a transaction.
The asset layer attributes to any token utilized in the DeFi application, including native protocol assets (generally ETH).
The protocol layer is the actual inner workings of the DApp (decentralized applications). It usually comprises a series of smart contracts that automatically manage the behavior of the assets utilized in the DeFi environment. It is vital to remember that although all smart contracts are governed by their own logic and always work based on this logic, they were originally written by humans, and it is possible that their code may contain bugs or loopholes that can be exploited.
The application layer is a user interface that makes it easy for people to interact with the DeFi platform. Without this layer, only those who are really good at blockchain and know how to program will be able to interact with DeFi.
The aggregation layer can be thought of as an extension of the application layer. Aggregators bring multiple applications together so that users can use a single dashboard to execute multiple types of DeFi transactions. The aggregator may be composed of pre-built decentralized applications, but it will likely take advantage of DeFi’s “financial building blocks” instead and allow people to choose which decentralized applications they want to aggregate to build their DeFi product suite. This is DeFi’s greatest strength. The level of aggregation allows DeFi as a whole to become more than the sum of its individual parts.
When a user wishes to interact with their decentralized applications, they can start by downloading their aggregator. This dashboard gives them access to some or all of the DeFi platforms they are currently using. Think of it as the home screen on your phone, where you have different icons for your favorite apps.
DeFi DApps
DApps differ from conventional apps in that they use blockchain as a database. DApps are used in a variety of areas, from gaming to sharing disk space or computing power, from marketplaces to social media. One of the areas of use for such applications is DeFi or decentralized finance. DeFi applications provide financial services similar to banks, but they do not have a centralized managing organization – the bank. The process of providing financial services is automated. Changes to this process are only possible by voting by users who own the platform’s management tokens. DeFi DApps use protocols and smart contracts for financial management and security.
DeFi applications have two types of tokens in operation – a control token and a token tied to the value of an asset. Control tokens are used to vote on changes to the application. Tokens that are tied to the value of assets are used for trading, accrual, and payment of interest, or are issued as a liability for which the collateral can be returned. They can be either stablecoins pegged to an asset at a 1:1 rate, or one can change their rate in relation to an asset.
For example, the Compound DeFi protocol uses COMP and aTokens. The latter is issued to the user when he or she provides a loan. The aTokens rate changes in accordance with the interest rate on the loan. Therefore, when the user returns them, the exchange takes place at a new rate. As a result, the protocol returns the collateral along with interest.
Liquidity Providers
When they build the DeFi project, they keep in mind it will work according to the following principle. There are users who provide liquidity – loans at interest, which are blocked in the protocol. Other users use this liquidity – for example, they take loans at interest. What makes DeFi special is that smart contract protocols automate these processes. DeFi does not require the consent of the other party to receive a loan or provide a loan – the process is automated and only certain conditions are required to complete a transaction.
For example, to obtain a loan, you must provide collateral in excess of the loan amount. This protects the protocol from the volatility of the cryptocurrency used as collateral. Another way to reduce volatility is to use DeFi protocols to create stablecoins, which are also backed by collateral in excess of their issuance amount.
DeFI Benefits and Use Cases
DeFi can perform all the same functions as traditional banks but much more efficiently and conveniently. The movement of decentralized finance makes it possible to use loans, open interest-bearing accounts, and trade without the need to trust centralized companies. Services are provided through decentralized applications (DApps), usually deployed on the Ethereum platform.
At the same time, it is absolutely not necessary to be an Ethereum specialist to use them, although it doesn’t hurt if you have a deeper understanding of the process. We can compare traditional and decentralized finance according to the main criteria: The system of payments and transfers. A bank transfer from one country to another can take days and involve a lot of fees. Moreover, there is a complete lack of privacy. The cryptocurrencies that underlie the work of DeFi development company do not need intermediaries and transfers are carried out as quickly as possible (on the Ethereum network, from 15 seconds, with a commission of about $0.02).
The benefits are clear:
- Availability. Banks impose strict restrictions on who can open an account, and even more so on the use of financial services such as lending. There are now more than a half-billion people in the world who do not have access to banking services. Defi is guaranteed to make their lives easier. To use an account, you only need the Internet.
- Centralization vs Decentralization. Banks are quite safe in terms of keeping funds, but not 100%. And the fall of a large bank will necessarily entail a large-scale financial crisis. DeFi protocols are managed by decentralized organizations, and this gives confidence that some people will not be able to make decisions on their own.
- Transparency. The average investor has no idea how his funds are used in a bank account. As for DeFi, the source code of the protocols developed on the basis of public blockchains is completely transparent for all users and open to audits.
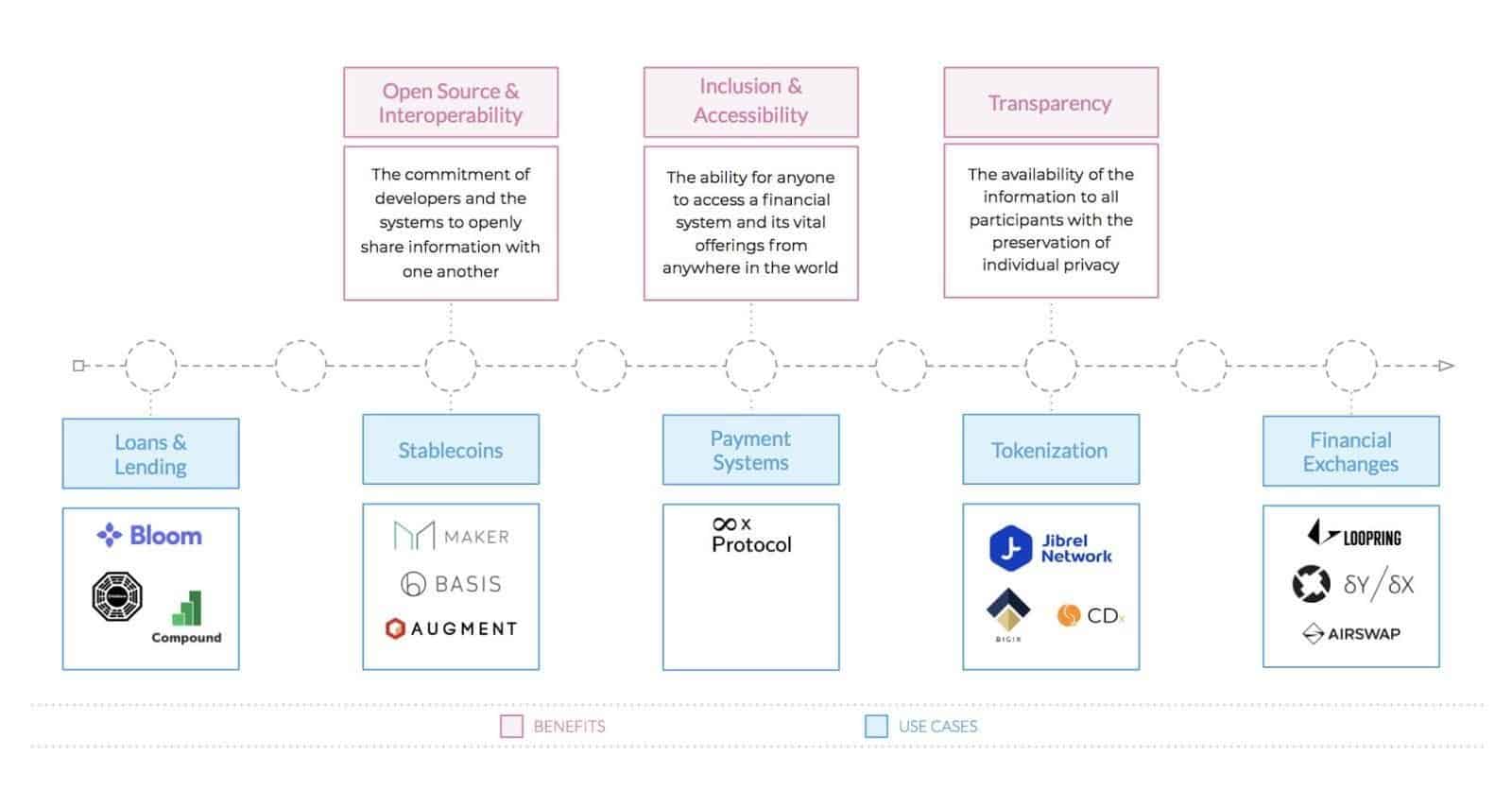
source: jibrel
Note: One of the most important possibilities that DeFi provides is decentralized identification. In the long term, DeFi development company with a decentralized identity can become an alternative for people deprived of access to the capabilities of conventional financial systems. There are billions of people around the globe without an official ID, and in poor countries, about 50% of women do not own one. But many of them have smartphones. Therefore, when decentralized identification systems start operating in developed countries, they can be implemented in developing countries as a breakthrough technology – just as it was with smartphones.
A vital benefit of building DeFi on smart contracts like Ethereum is interoperability. By analogy with libraries of software modules, smart contracts of various financial applications can be combined like designer parts. For instance, if you desire to implement the tokenized assets trading option on your platform, you can simply achieve this by deploying a decentralized exchange protocol. Using such a “constructor,” you can also generate entirely unique designs, which is unknown in the traditional world.
Oracles: Trusted Data Sources
In order to better understand DeFi, you need to realize how different tokens function in the cryptocurrency ecosystem. Let’s explore the basics of oracles first.
Oracle is an agent that finds and confirms real events and transfers this data to the blockchain to use smart contracts. Smart contracts need oracles to highlight details that may not be uniquely known and understood at the time of writing.
For instance: Alice and Bob are betting on the temperature on Saturday. Alice thinks the temperature will be 20° C or higher, and Bob thinks the temperature will be 19° C or lower. They develop a smart contract with which both send the funds that must be paid to the winner. To define the temperature, the smart contract must request a reliable resource – oracle. In this particular case, the smart contract will resort to the weather news website, which will be the oracle.
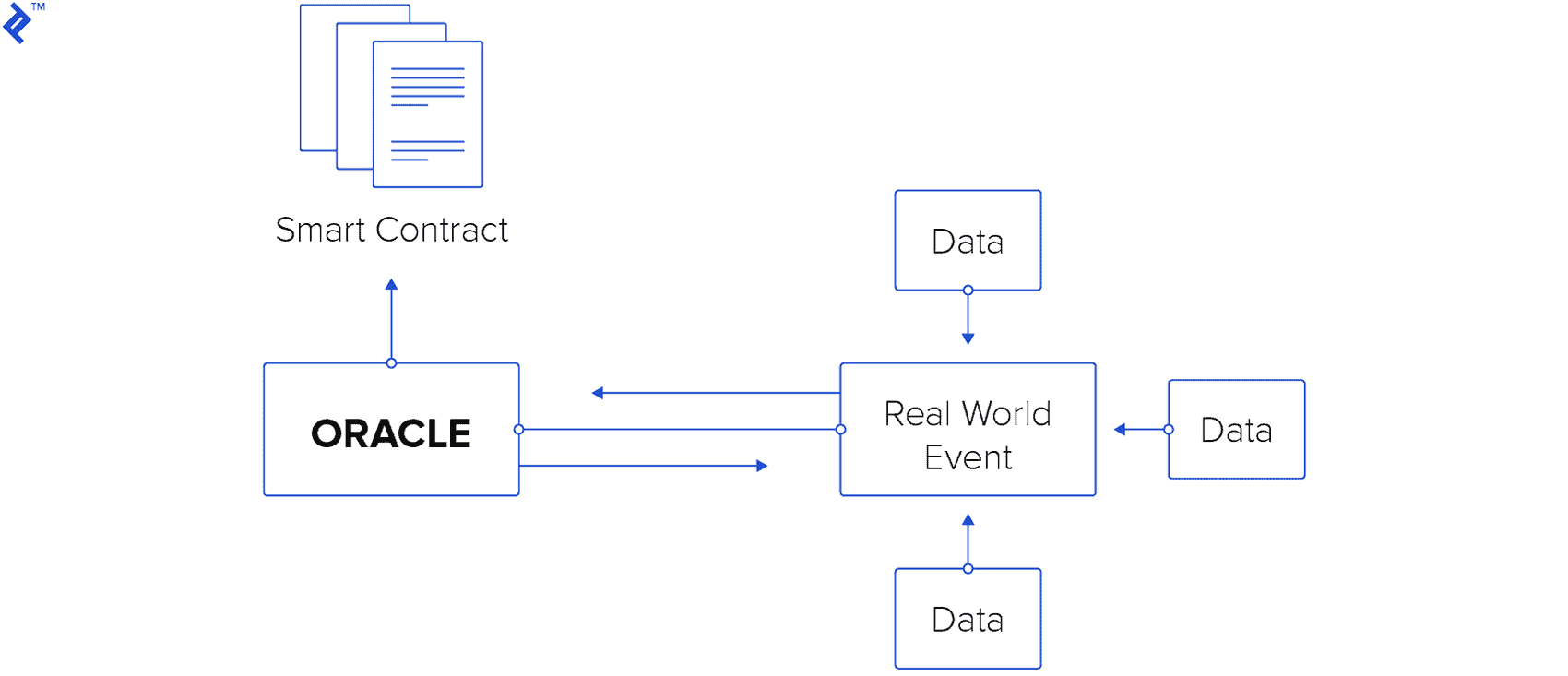
Source: toptal.com
Oracles are used in various areas of blockchain product development where smart contracts are utilized. But oracles are especially popular and most actively used in DeFi projects. Moreover, this connection is so strong that many crypto observers list oracle tokens in the DeFi token group.
The most bright examples of using oracles in DeFi are:
- Synthetic asset platforms require real asset prices to be displayed on the web. Oracles are used to create tokens that are tied to real assets such as gold, indices, stocks, or cryptocurrencies.
- Lending and borrowing platforms require the participation of oracles to guarantee the full value of the collateral. Used for issuing and repaying loans, repaying collateral, and calculating interest payments.
- For stablecoins, a price stream is required to confirm the value of the underlying asset’s collateral. They are used to create stablecoins pegged to fiat currencies, currency baskets, or commodities.
The undisputed leader among all oracles can be considered the ChainLink blockchain. It is a pioneer in the provision of reliable data for DeFi, and its LINK token and is currently ranked as the number one oracle token, with a capitalization of $ 5.86 billion. After the price fell in March of this year due to the pandemic, the token fully recovered, and in July it reached a historical maximum. It has been growing exponentially since then. The increase in prices since the beginning of this year was 463%. This is the largest increase among the top coins.
Asset Tokenization
Tokenization opens the door to the DeFi ecosystem for assets that were previously unable to access it. It opens up new possibilities with its asset-backed composability.
The fundamental goal of tokenization is to bring accessibility to asset holders and make transactions more effective. Tokenized assets can be smoothly transferred to anyone in the world in a matter of seconds. They can be utilized in many decentralized apps and held in smart contracts. These tokens are an important part of the DeFi ecosystem.
The process of adding new assets to the blockchain (public blockchains) is called tokenization, and the representation of an asset on the blockchain product development system is called a token. From a technological point of view, there are numerous ways to create public Blockchain tokens. However, most of these options can be neglected as most tokens are issued on the Ethereum blockchain using a smart contract template called the ERC-20 token standard. These tokens can be applied in almost all DeFi apps.
Benefits of Tokenization
The financial market is full of various assets. Tokenization of physical assets is changing the paradigm of managing them offering benefits that were previously impossible. Some of them are described below.
Programmability. Programmable money is an advantage of tokenization, which, again, is central to blockchain assets and completely absent from traditional financial alternatives. The ability to program items of value to move from one person or organization to another owner, if and only if certain conditions are met, has excellent potential for creating items of value and significantly reducing operating costs. A simple first example would be a tokenized share, which distributes a percentage of its net income in the form of a quarterly dividend only among those token holders whose quarterly net profit is positive. Pre-programming this dividend function will significantly reduce the manual and time-consuming process of issuing quarterly dividends. A somewhat more complex example would be tokens that are converted between equity and debt instruments based on predefined parameters. The transparency of the public chain of blocks will allow anyone to confirm the correct operation of the protocol.
Fractional Investment. Fractional ownership will open new asset classes for the average investor and make smaller investment amounts possible. As an example, purchases of art objects are usually conducted through a closed bidding process as opposed to the public market process, which leads to sole ownership (one owner per asset) instead of shared ownership (many co-owners of one asset). For something like Mona Lisa, owning an auction market alone would essentially represent one “Mona Lisa share” worth $800 million. Market-share holdings could potentially represent 10 million shares of Mona Lisa, valued at $80 each. Since there are many more people on Earth who can afford to spend $80 to buy a famous work of art, a liquid market of buyers and sellers will appear, which will make trading faster and cheaper. Compare this with the slow and expensive illiquid method: today you have to look for the only buyer who wants and is able to spend $800 million to buy a painting. This also concerns real estate investments.
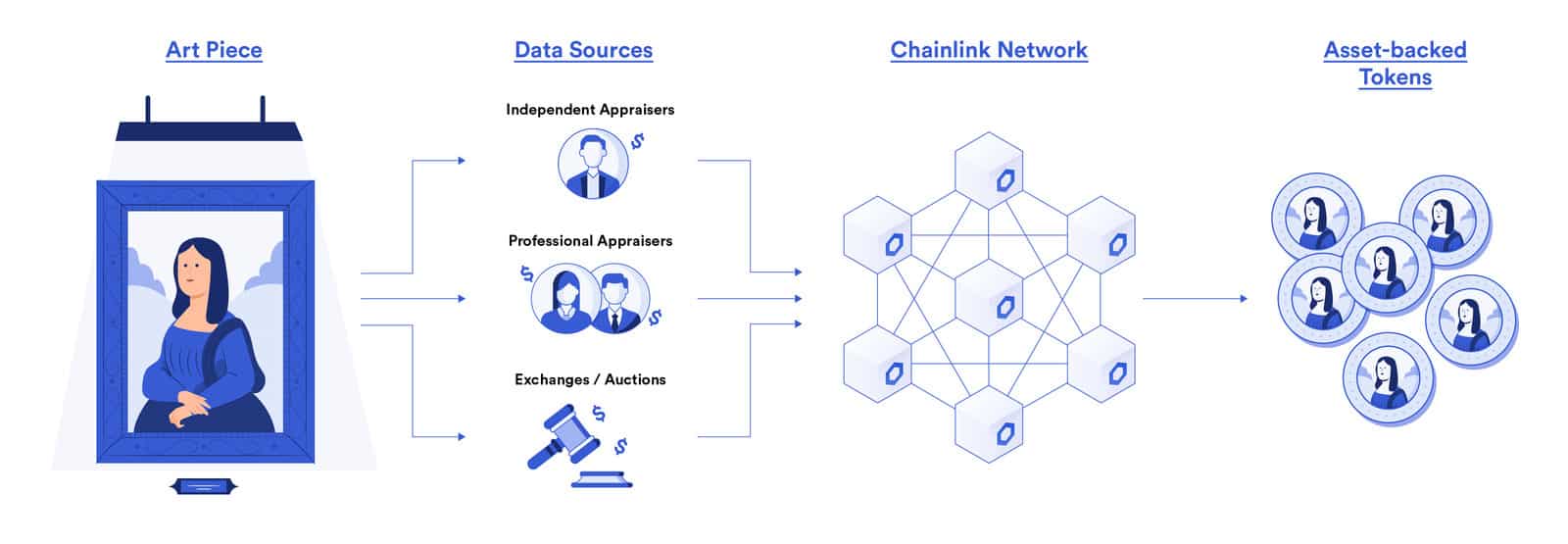
source: chain.link
Liquidity. As indicated in the Mona Lisa example, fractionation can contribute to more favorable liquidity on the part of buyers and sellers, which allows them to carry out transactions without any problems. For clarity, the tokenization process itself does not increase the liquidity of an asset, but the increase in the number of potential buyers and sellers, due to the share ownership function of an asset due to tokenization, contributes to this effect. Since investors in illiquid assets take the risk of not finding a buyer, they need to motivate the buyer with a reduced price, known as the “discount for illiquid assets.” This discount applies to all illiquid assets and is estimated at 20-30% of the true price of assets. Through the tokenization process, it is possible to optimize markets for previously illiquid asset classes and increase true value.
Portfolio Management
Portfolio management is the process of overseeing your assets and managing their cash flow to generate returns on your investments. There are two main types of portfolio management – active and passive. Active portfolio management requires a team of portfolio managers making investment decisions to generate returns that are greater than a certain benchmark, such as the S&P 500. Passive portfolio management does not require such a team; it involves mimicking the return of a certain benchmark as much as possible. In DeFi, some projects already allow passive portfolio management on a decentralized basis. DeFi’s transparency allows users to easily track how their assets are being managed and understand the costs they will incur.
Lending and Loans
Traditional financial systems require users to have bank accounts in order to use their services – a luxury that about 2 billion people currently lack. Obtaining a loan from a bank comes with other constraints such as having a good credit rating and having sufficient collateral to convince the bank that the borrower deserves the loan and is able to repay it. Decentralized lending and borrowing remove this barrier by allowing anyone to use their digital assets as collateral to obtain loans. You can also generate income from your digital assets in the lending market by contributing these assets to loan pools and earning interest on it. With decentralized lending and borrowing, there is no need for a bank account or credit check.
Insurance
Insurance is a risk management strategy whereby a person receives financial protection or compensation from an insurance company in the event of an accident. Usually, people buy insurance for cars, homes, health, and life. But is there decentralized insurance for DeFi? All tokens involved in smart contracts are potentially vulnerable to hacker attracts. Although the code of most projects has been audited, you can never know if their smart contracts are truly completely secure. There is always the possibility of a break-in, which can lead to losses. These risks lead to the need to buy insurance, especially if you operate with large amounts.
Exchanges
You can use exchanges such as Coinbase or Binance to exchange one cryptocurrency for another. Such exchanges are centralized, they act as both intermediaries and custodians of traded assets. Users of these exchanges do not have full control over their assets, which puts their assets at risk if the exchanges are hacked and fail to pay off their obligations to users. Decentralized exchanges solve this problem by allowing users to exchange cryptocurrencies without having to transfer their coins to a custodian. When users don’t store their funds on centralized exchanges, they don’t need to trust those exchanges to stay solvent.
Derivatives
A derivative is a contract whose value is derived from another underlying asset, such as stocks, commodities, currencies, indices, bonds, or interest rates. Traders can use derivatives to hedge their positions and reduce risk in any trade. Derivatives are mainly traded on centralized platforms. DeFi platforms are starting to create decentralized derivatives markets.
Stablecoins
Cryptocurrency rates are extremely volatile. To mitigate this volatility, stablecoins were created and pegged to various stable assets, in particular the US dollar. Stablecoins help users hedge against cryptocurrency volatility and are designed to act as a reliable medium of exchange. Stablecoins have quickly grown into a powerful DeFi component that plays a key role in this modular ecosystem. There are currently 33 stablecoins on CoinGecko. The top 5 stablecoins have a total market cap of over $25 billion.
Decentralized stablecoins are designed to address this trust issue: they are issued by decentralized over-collateralization, operate in decentralized ledgers, and are managed by decentralized autonomous organizations. Also, their reserves can be publicly verified by anyone. While stablecoins are not a financial application per se, they are important because having a stable store of value helps make DeFi applications more accessible to everyone.
Not all stablecoins are the same as they use different mechanisms to maintain their peg to the US dollar. There are two main types of stablecoins, namely backed by local currencies and backed by cryptocurrencies. Most stablecoins use a local currency backing system to maintain their peg to the US dollar.
Important: Why do protocols need collateral?
In order to reduce risks.
For example, do you want to receive stable currency Dai in exchange for volatile ETH with the ability to get your ETH back at its original price when it grows up? To do this, you need to deposit ETH in a ratio of 1 to 1.7. That is, for every dollar in Dai, you need to deposit $ 1.7 in ETH. This is to ensure the operation and security of the protocol.
Many other lending protocols work in a similar way. To get a loan, you must already be a member of the crypto economy and post collateral. Loans without collateral in a decentralized world are impossible until the concept of distributed reputation and identity emerges. In other words, while it is impossible to conduct credit scoring of anonymous wallets based on the history of their behavior, all credit relations will be based on the full bank reserve model.
Who manages the protocols?
It all depends on the specific protocol and the stage of its development. At launch, developers tend to retain a significant degree of influence over the protocol and its participants. They have a red button.
With development, many protocols are transferred to user control. For this, tokens are used that give the right to vote. For example, the MKR token gives the right to vote on what assets can be accepted as collateral for the issue of the Dai stablecoin. While the Synthetix derivatives platform is managed by three DAOs, where SNX holders have voting rights.
Dai Vs Sai
Sai (SAI) is also known as Single-Collateral Dai – it is backed exclusively by Ether (ETH) as collateral. Maker began its work on December 19, 2017, with the launch of this mono-collateral Dai. On November 18, 2019, Maker announced the launch of a new multi-collateral Dai, issued to back up Ether (ETH) and/or Basic Attention Token (BAT), as well as other cryptocurrencies. Going forward, multi-collateral Dai will be the de facto stablecoin standard supported by Maker, and eventually Sai will be phased out and no longer supported by Maker.
How does Maker ensure user value?
The black swan is an unpredictable and extreme event that can have serious consequences. In the event that ETH and BAT drop significantly in value, Maker can initiate an Emergency Shutdown. It is a process used as a last resort to settle the Maker platform by closing all positions in the system.
The Difference Between DeFi and Fintech
In fact, decentralized finance can easily be confused with financial technology. Both systems operate over the Internet and provide financial services without the involvement of banks and other traditional financial institutions. However, there are several fundamental differences between the two markets. One of the main differences is that fintech is bringing the traditional financial system to the internet, while decentralized finance is built on the blockchain.
Fintech giant Square is a payment system that offers faster and cheaper cross-border payments compared to traditional banks. However, at the same time, the company’s platform operates with the participation of a central authority in the person of Square itself. The site carries out transactions on behalf of its customers, who are required to provide reliable identification data before opening an account.
In the case of DeFi, it looks different. Dai is an Ethereum-based stablecoin pegged to the US dollar. A user who makes a transaction with this currency does not need to trust a particular organization to carry out the transaction. Instead, the transaction is confirmed by miners on the Ethereum blockchain
A Step Back From the ICO World
Native tokens of a DeFi development company are becoming an important tool for incentivizing participants, and at first, only ordinary tokens were issued, but recently the emergence of digital assets (governance tokens) has been observed, which can provide rights to participate in the work of the site. These are Yearn.finance, UNI (Uniswap), etc. The emergence of such governance tokens can be attributed to the fact that, unlike the ICO boom, investors want to have an instrument of direct influence on the project implementation process.
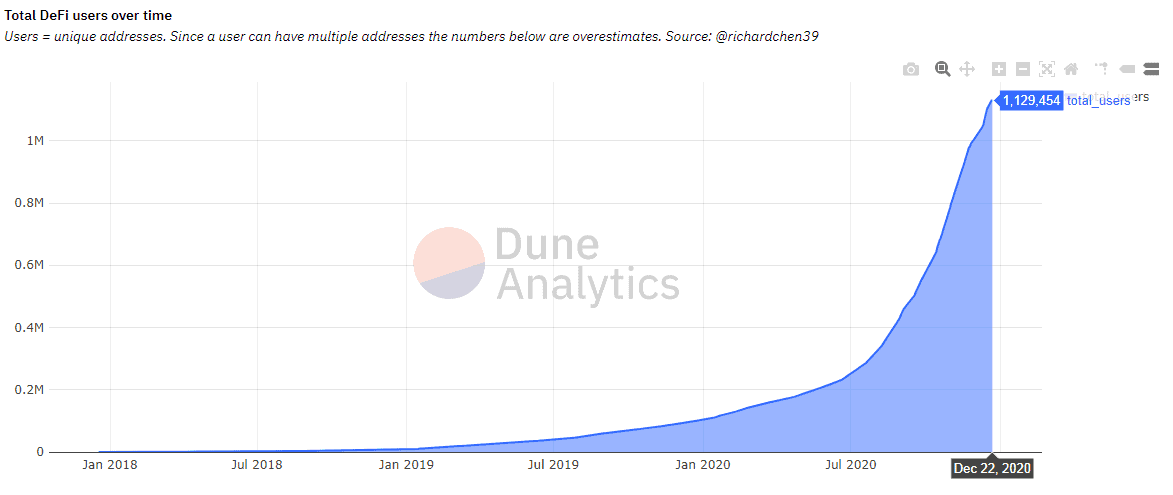
source: Dune Analytics
Formally, DeFi development company has taken a big step up from ICO projects. If ICO is a story that investors were forced to trust people who organize the issuance of certain tokens, then DeFi is a technological system that is based on smart contracts, and not on human decisions. This should potentially give a higher level of investment security.
Eliminating Problems of Traditional Finance
DeFi is a movement aimed at solving the main problems of traditional finance: low transaction speed, regulatory control, high fees, limited availability. It is able to eliminate these differences and provide access to financial transactions to everyone without any type of censorship. Applicature identifies the following important advantages of Decentralized Finances:
- Decentralization, thanks to which control over the ecosystem belongs to all participants at once, transactions are fast and transparent;
- There are no intermediaries;
- Management via smart contracts;
- Open source code, which can be checked and modified at any time, as well as used to form other services based on them;
- Speed and low cost of operations in decentralized networks;
- The immutability of the contracts recorded in the blockchain;
- Transparency and openness to audit;
- Lack of centralized management-everything works on smart contracts programmed in advance;
- No one can imperceptibly edit the contract in their favor; and
- The DeFi market is available to anyone with the Internet, regardless of country of residence or other factors.
DeFi Risks and Hazards
Despite all the advantages, there are also dangerous sides of decentralized finance. This is understandable since the technology is relatively new. The main risks include:
- Hacking smart contracts. The code is written by a person, and it is human nature to make mistakes. It makes sense to use only those platforms that have been verified by well-known auditors, although even then there is a small chance that you missed an important mistake.
- Liquidity and credit risks. The cryptocurrency is volatile, and the system may collapse if the underlying asset falls sharply. DeFi protocols try to combat this problem by over-collateralized loans.
- Lack of funds for lending. With specific collateral in DeFi, you can get a more modest loan compared to one from a traditional financial institution.
- Fake oracles. Blockchain protocols receive data (cryptocurrency rates, etc.) from external systems, which are often centralized. If the source is unreliable, then the smart contracts will be executed incorrectly. To eliminate this risk, decentralized source alternatives are being developed.
- Centralized control over development. Whatever one may say, one team is engaged in the creation of the code. In more and more cases, DeFi developers involve users in the process, but this can cause problems due to incompetent intervention. It is difficult to find a responsible person. The principle of decentralized governance does not always work out the way it was originally intended. All users are equal, but among them, there are those who aim to collapse the ecosystem, or are simply passive and not going to participate in the process (which often does no less harm than the actions of intruders).
Nevertheless, there is a lot of buzz around DeFi at the moment. The sphere seems extremely promising and many companies are already implementing DeFi solutions into their range of services or planning to do so. Cointelegraph conducted a survey in 2020, and the results are amazing. Almost 50% of already existing platforms are planning to offer DeFi custom business services. So, if you ever wanted to launch a DeFi project, right now is the perfect timing.
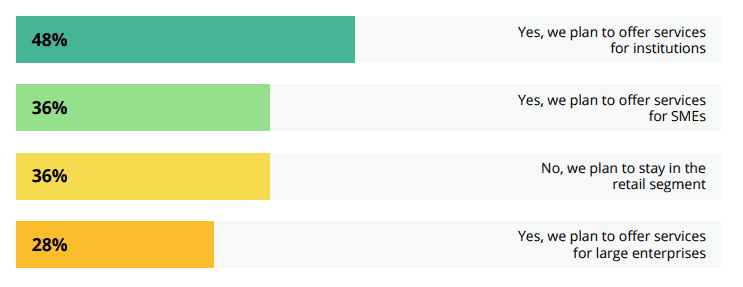
Source: Cointelegraph Consulting DeFi Survey 2020
Final Word
The topic of decentralized finance is almost endless, we only covered the main aspects. Today, hundreds of applications in this area have been created and are successfully working. Some have become very popular in a matter of months, like Compound or Uniswap. The potential of DeFi has not been ignored by large companies. For example, the Binance exchange found it necessary to launch a decentralized platform, Binance DEX.
DeFi applications and projects can be extremely useful to residents of countries with weak or unstable economies. For example, in Argentina, it was even proposed to give people a salary of DAI due to the horrific inflation of the national currency. Services are in demand in developed countries as well, since they offer a more profitable and affordable lending system and open up new opportunities for interest income from investments.
Efficient and transparent financial services are essential for engaging users in the ecosystem, and unlike the failed attempts of the traditional financial system, decentralized finance is making strides in bringing about the necessary paradigm shift.
When DeFi is fully matured, the use of libraries outside of the crypto community should be expected. You can add just one line of code and a completely decentralized marketplace will appear in the video game. Or add an extra line to enable retailers on a commercial site to gain benefit on balances.
The general opinion of leading economic visionaries is that blockchain is the fundamental technology of the digital economy, on the basis of which an inclusive society of mutual creativity and trust will be built. Applicature is one of the pioneers in the sphere. If you want to launch a DeFi project, audit smart contacts, or need any support with your blockchain platform, Applicature is at your service!

 NEM Blockchain Review
NEM Blockchain Review
 Blockchain API Utilization
Blockchain API Utilization
 Crypto-Investor Day: New Strategies for Security Tokenization
Crypto-Investor Day: New Strategies for Security Tokenization
 Lightning-Fast Bitcoin Transactions
Lightning-Fast Bitcoin Transactions
